Step 1: Define scenarios based on strategic environment (PESTLED).
PESTLED analysis is a strategic tool used to analyze the external factors that can impact an organization’s performance. PESTLED stands for political, economic, sociocultural, technological, legal, environmental, and demographic factors. Based on the key drivers, individuals and organizations can create scenarios. A scenario is a plausible and coherent description of a potential future situation or event that is constructed to help individuals or organizations prepare for and respond to a range of possibilities.
Individuals and organizations typically develop scenarios by considering multiple factors and variables that may influence a particular situation or outcome (the key drivers). Individuals and organizations can use these key drivers as a strategic planning tool to explore different options and anticipate potential challenges and opportunities—what we call strategic initiatives—that may be of great importance in the future.
Political:
- A new government is elected that implements stricter regulations on businesses, leading to increased compliance costs and lower profits.
- A trade war between two countries results in higher tariffs and reduced demand for goods and services.
- The government introduces a new tax policy that increases taxes on certain industries, leading to reduced investments and slower growth.
Economic:
- A recession occurs, leading to decreased consumer spending and lower demand for products and services.
- The inflation rate increases, resulting in higher costs of production and decreased profits.
- The interest rate increases, making it more difficult for businesses to borrow money and invest in new projects.
Sociocultural:
- Changes in consumer preferences lead to a shift in demand for certain products, such as a preference for plant-based foods over meat-based products.
- Demographic changes, such as an aging population, lead to increased demand for healthcare services.
- Social trends, such as increased awareness of environmental issues, result in changes in consumer behavior and increased demand for eco-friendly products.
Technological:
- A new technology disrupts the market and makes traditional products or services obsolete.
- Cybersecurity breaches occur, leading to a loss of consumer trust and reduced demand for online services.
- Advancements in automation technology lead to increased efficiency and reduced labor costs.
Legal:
- Changes in labor laws result in increased labor costs and reduced profitability for businesses.
- New regulations on data privacy result in increased compliance costs for companies that collect and store personal data.
- Intellectual property disputes can lead to costly legal battles and damage to a company’s reputation.
Environmental:
- Natural disasters, such as hurricanes or floods, result in supply chain disruptions and increased costs for businesses.
- Increased awareness of environmental issues leads to increased demand for sustainable products and services.
- Government regulations on carbon emissions increase costs for businesses and lead to changes in product design and production processes.
Demographic:
- Changes in population demographics, such as an aging population, lead to increased demand for certain products or services, such as healthcare or retirement homes.
- Changes in immigration policies lead to changes in the labor force and increased competition for jobs.
- Changes in birth rates impact demand for products and services targeted toward families, such as baby products or family vacations.
Step 2: Based on scenarios, define strategic initiatives
Strategic initiatives for innovation are specific actions or potential future projects that organizations undertake to improve their ability to innovate and stay competitive. The organization typically designs these initiatives to address specific challenges or take advantage of specific opportunities. Here are some characteristics that describe strategic initiatives for innovation:
- Strategic initiatives for innovation are aligned with the organization’s overall strategy. The organization will align the strategic initiatives for innovation with its overall strategic objectives. They are designed to support the organization’s long-term goals and to help it achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
- Strategic initiatives involve cross-functional collaboration. Strategic initiatives for innovation typically involve collaboration between different functions or departments within an organization. This may include R&D, marketing, operations, and other teams working together to develop new ideas and bring them to market.
- Strategic initiatives are based on a clear understanding of needs. The organization typically bases the strategic initiatives for innovation on a clear understanding of customer needs and preferences. This may involve conducting anthropological research or gathering customer observations to ensure that the organization is developing products or services that meet customer needs.
- Strategic initiatives should be measurable. This means that the organization can track progress toward its goals and determine whether the initiative is achieving the desired results.
- Strategic initiatives involve risk-taking and exploring new ideas. This may require the organization to step outside of its comfort zone and try new approaches that may not have been tried before.
- Strategic initiatives often require investment. These investments could be time and/or resources. This may involve dedicating personnel to work on the initiative or investing in new technologies or infrastructure to support the initiative.
- Strategic initiatives involve continuous improvement. The organization must continually assess the success of the initiative and make adjustments as necessary to ensure that it remains effective and relevant over time.
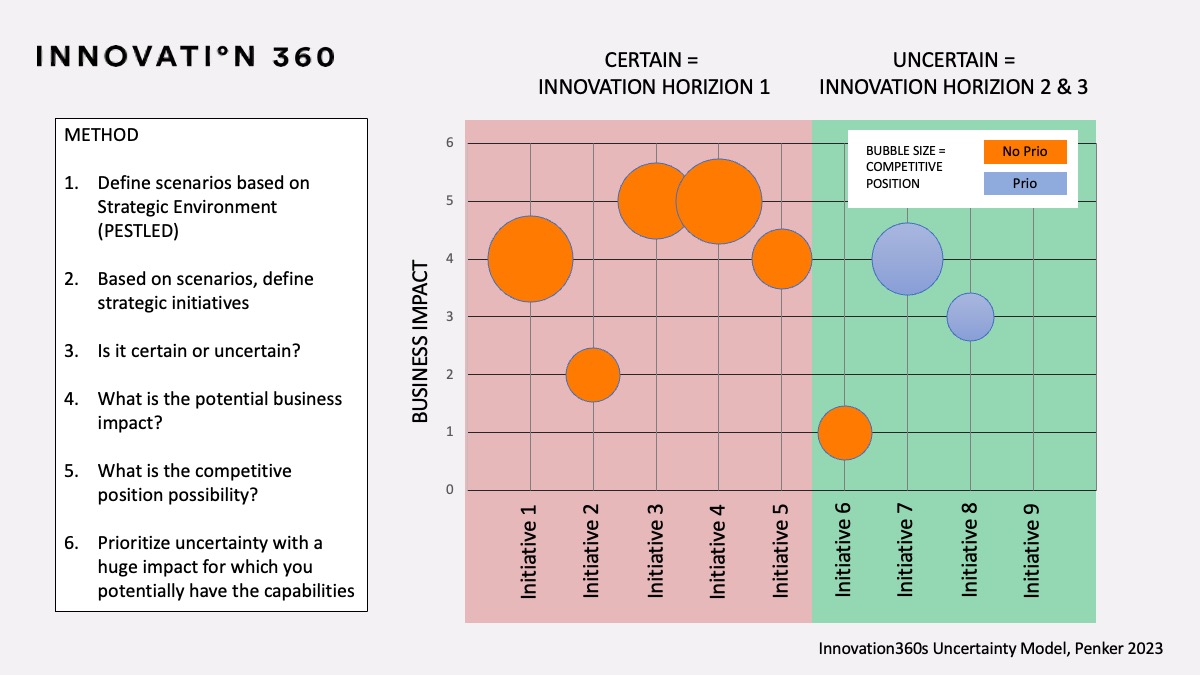
Step 3: Is it certain or uncertain?
Certain market opportunities are highly predictable and have a high degree of certainty. These opportunities are typically based on existing trends or established patterns in the market, and the likelihood of success is relatively high. For example, if there is a growing demand for organic food products in the market, an organic food producer could launch a new line of organic products with a high degree of certainty that they will be successful.
On the other hand, uncertain market opportunities are less predictable and have a higher degree of risk. These opportunities are often based on emerging trends or new technologies that are not yet well-established in the market. Pursuing these opportunities requires taking risks and investing resources into untested areas. For example, investing in a new technology that is still in the early stages of development carries a higher degree of uncertainty and risk.
Although certain market opportunities may be easier to pursue, they may also have limited growth potential and may be vulnerable to competition. Uncertain market opportunities may offer greater potential for growth and differentiation, but they also carry higher risks of failure. Organizations should carefully consider both types of opportunities and assess their risk appetite and capability to pursue them. A balanced approach that considers both types of opportunities can help organizations achieve sustainable growth and long-term success.
Step 4: What is the potential business impact?
Potential business impact refers to the expected effect that a specific project or initiative will have on an organization’s bottom line. It involves predicting how the project or initiative will impact key performance indicators such as revenue, profits, market share, customer satisfaction, or employee retention.
To define the potential business impact, the organization should clearly identify the specific goals and objectives of the initiative. This may involve defining specific metrics or key performance indicators that you want to measure. For example, if the goal of the project is to increase customer satisfaction, then the organization could define the potential business impact in terms of the expected increase in customer retention or loyalty.
Once the organization has defined the specific goals and objectives, the organization should assess the potential impact on the organization’s bottom line. This may involve analyzing historical data and industry benchmarks, or conducting sensitivity analysis to estimate potential changes in performance. By carefully assessing the potential business impact, organizations can make informed decisions about which projects or initiatives to pursue and how to allocate resources to maximize their return on investment.
Potential business impact is not a guarantee of actual results. Many factors can impact the success of a project or initiative, including internal and external factors such as competition, economic conditions, and regulatory changes. Therefore, organizations should regularly monitor and evaluate the actual impact of the project or initiative and adjust accordingly to ensure that it is achieving its goals and objectives.
Step 5: What is the competitive position possibility?
Potential competitive advantage refers to the ability of a company or organization to outperform its competitors by offering better products, services, or processes. It is the advantage that a company has over its competitors to create and sustain customer value.
To describe potential competitive advantage, organizations should consider the unique strengths and capabilities of the organization. This may involve evaluating factors such as brand reputation, intellectual property, supply chain efficiency, customer service, or technological innovation.
After the organization has identified its unique strengths and capabilities, describe the value creation outperforming the competitors. This may involve developing new products or services, improving existing processes or systems, or adopting new technologies.
One way to describe potential competitive advantage is to identify the key factors that differentiate the organization from its competitors. An example is a reputation for exceptional customer service.
Another way to describe potential competitive advantage is to assess how it can be sustained over time. This may involve developing barriers to entry, such as patent protection or economies of scale, that make it difficult for competitors to replicate the organization’s strengths and capabilities.
Ultimately, potential competitive advantage is a key factor in driving an organization’s long-term success and profitability. By understanding and leveraging their unique strengths and capabilities, organizations can create value for customers and outperform their competitors in the marketplace.
Step 6: Prioritizing and managing uncertainty with a huge impact for which you potentially have the capabilities.
It can be challenging for organizations to prioritize uncertain scenarios with huge potential impact for which it has the capabilities. Here are some steps to help with this process:
- Start with the uncertain scenarios. This may involve conducting a thorough analysis of the external environment. It include factors such as market trends, technological advancements, or regulatory changes and other key drivers.
- Assess the potential impact: Once the organization has identified uncertain scenarios, it should assess the potential impact on the organization. This may involve estimating the potential financial, operational, or strategic impact of each initiative.
- Evaluate capabilities: Next, the organization should evaluate its capabilities to address each scenario. This is typically done by assessment like Inovaton360’s InnoSurvey or an equivalent.
- Prioritize the initiatives: After assessing the potential impact and the organization’s capabilities, it is important to prioritize the uncertain initiatives. This may involve using a risk matrix or other prioritization tool to rank the initiatives. The ranking is based on their potential impact and the organization’s capabilities to address them.
- Develop action plans: Finally, organizations should develop action plans for the prioritized initiatives. This may involve Innovation Sprints to get a deeper understanding, allocating resources, and establishing timelines and performance metrics.
Sum summarize, prioritize uncertain scenarios with a huge potential impact for which they have the capabilities. This way organizations can better manage risk over time and capitalize on opportunities.